Devoted to Spectroscopy
Our Core Technologies
Our team has been working with laser technology for over 20 years. This experience gives us in-depth knowledge of various optical spectroscopy techniques.
・Raman Scattering Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique in material science, chemistry, and biology. It provides detailed molecular information by detecting vibrational modes of molecules without requiring extensive sample preparation, which preserves the sample’s integrity. The method is non-destructive and works well on solids, liquids, and gases, even through transparent containers like glass or plastic. Unlike infrared spectroscopy, Raman can be applied in aqueous environments because water produces a weak Raman signal, making it ideal for biological and medical applications. Additionally, modern Raman instruments enable in-situ and remote measurements, micro-scale spatial resolution, and compatibility with fiber optics for flexible, real-time analysis, all without the need for labeling or complex processing.
・Hyperspectral Imaging
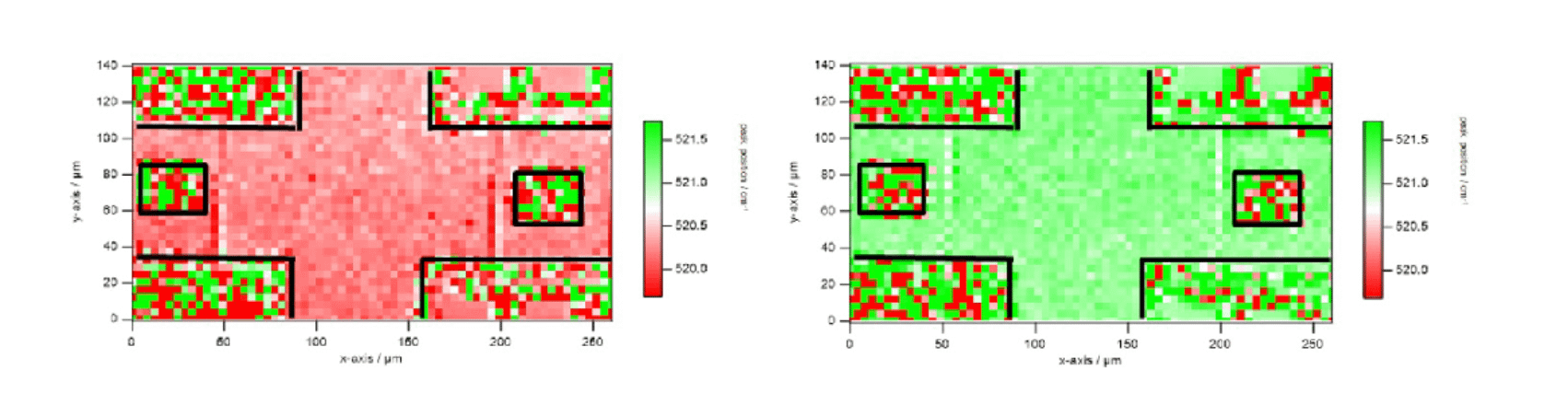
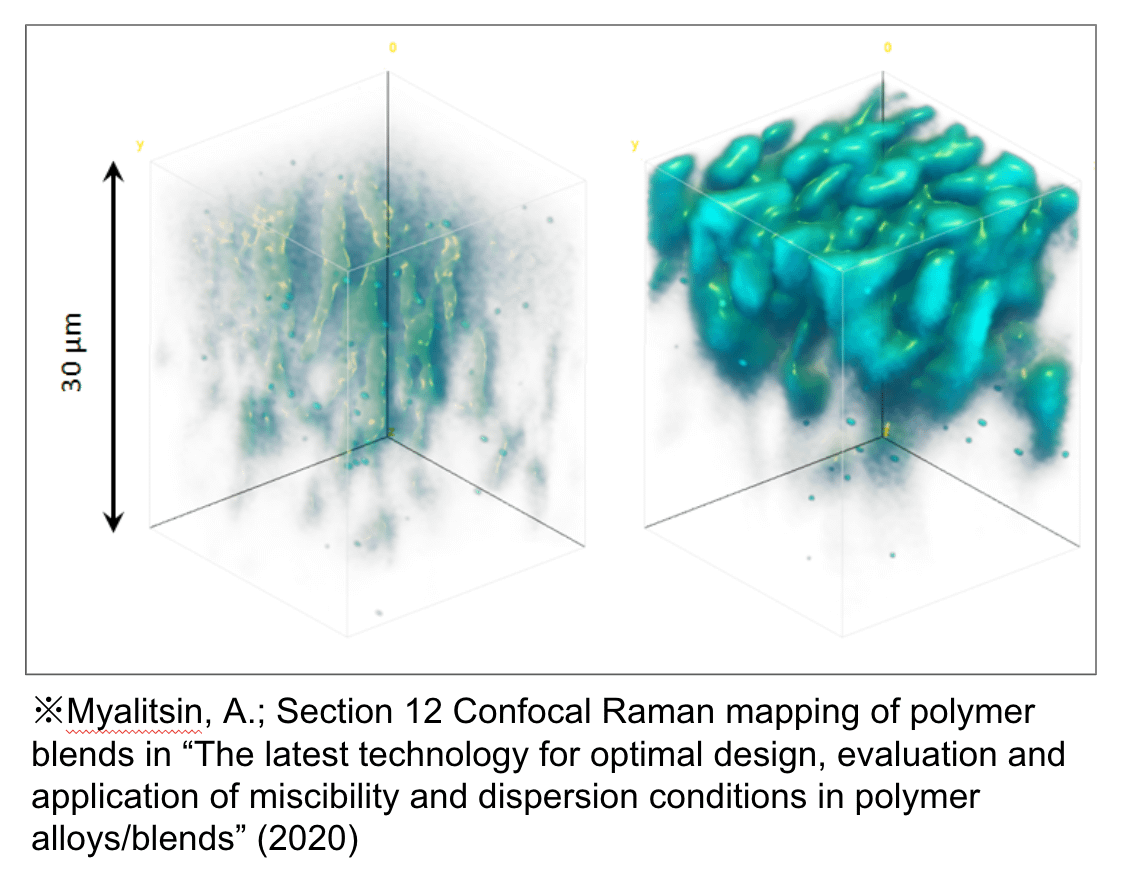
Hyperspectral Raman imaging combines the chemical specificity of Raman spectroscopy with spatially resolved imaging, enabling the creation of detailed chemical maps of a sample at microscopic scales. In this technique, a Raman spectrum is collected at each pixel across a sample, producing a hyperspectral dataset that contains both spatial and spectral information. This allows for precise identification and distribution mapping of different molecular species within heterogeneous materials, making it invaluable in fields such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and biomedical research. Unlike conventional imaging methods that rely on color or intensity contrast, hyperspectral Raman imaging reveals molecular composition and structure, even in complex mixtures, without the need for dyes or labels. Its ability to provide both qualitative and quantitative information in a non-destructive, label-free manner makes it a powerful tool for advanced analytical applications.
Information that can be obtained: component analysis, residual stress distribution (e.g. semiconductors, injection molded plastics), charge density distribution in doped semiconductor wafers, 3D imaging, etc.
・VSFG(Vibrational sum frequency generation spectroscopy)
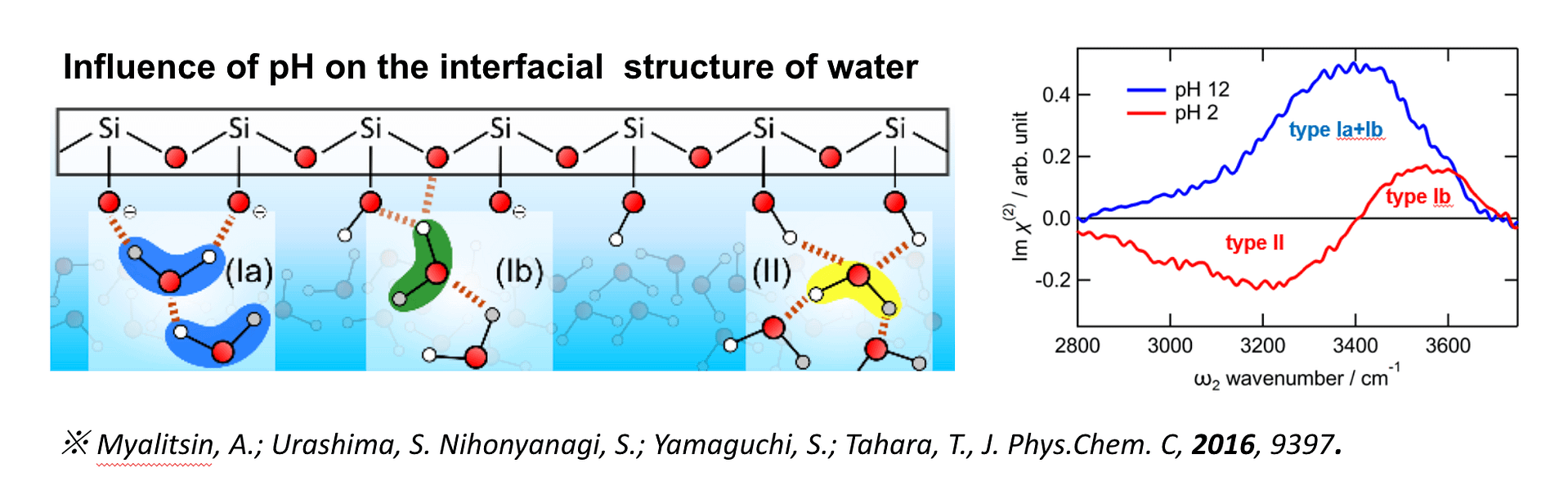
Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation (VSFG) is a powerful nonlinear optical spectroscopy technique used to probe molecular vibrations at interfaces with exceptional surface specificity. It relies on the simultaneous interaction of two laser beams—typically one in the visible range and one in the infrared—that combine at an interface to generate a signal at the sum of their frequencies. Because VSFG is only allowed in non-centrosymmetric environments, it inherently excludes bulk contributions in centrosymmetric media, making it highly sensitive to surfaces and interfaces such as those in catalysis, biological membranes, and thin films. This label-free and non-destructive technique provides detailed vibrational information, making possible to investigate molecular orientation, structure, and dynamics at buried interfaces that are often inaccessible by other methods. Its unique interfacial selectivity and ability to operate under realistic conditions have made VSFG indispensable for studying chemical processes at surfaces.
We provide highly accurate SFG spectrometry services and expert support for data analysis. With cutting-edge technology, we strongly support our customers’ research and development.
・SERS (Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy)
SERS (surface-enhanced Raman scattering) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique that allows for highly sensitive detection of trace substances.
By utilizing nanostructured surfaces, it is possible to clearly identify extremely small amounts of molecules and chemical species that are difficult to detect using conventional Raman spectroscopy.
This will enable more accurate and efficient analysis, and is expected to be applicable in a variety of fields, including environmental monitoring, medical diagnosis, and rapid detection of chemicals.
・SEIRAS (Surface-enhanced Infra-Red Absorption Spectroscopy)
Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy (SEIRAS) is a highly sensitive vibrational spectroscopy technique that amplifies infrared absorption signals of molecules adsorbed on nanostructured metallic surfaces, typically gold or silver. The enhancement arises from localized surface plasmon resonances and electromagnetic field confinement at the metal surface, which significantly increases the interaction between infrared light and the adsorbed molecules. SEIRAS is particularly useful for studying thin films, surface reactions, and biomolecular interactions at interfaces because it combines high surface sensitivity with molecular specificity. Unlike conventional IR spectroscopy, SEIRAS can detect sub-monolayer coverage and monitor dynamic processes in real time under electrochemical or catalytic conditions, making it an invaluable tool in surface science, electrochemistry, and biomolecular research.
・Brillouin Scattering Spectroscopy
Brillouin scattering spectroscopy is an optical technique used to study acoustic phonons and mechanical properties of materials by analyzing the inelastic scattering of light. When a laser beam interacts with these phonons, a small frequency shift occurs in the scattered light, providing information about sound velocity, elastic moduli, and viscoelastic properties at the microscopic scale. This non-destructive method is highly sensitive to mechanical characteristics such as stiffness and compressibility, making it valuable for investigating solids, liquids, and biological samples. Brillouin spectroscopy can probe buried layers and transparent media with high spatial resolution when combined with microscopy, offering unique insights into nanomechanics, thin films, and even living cells under physiological conditions without requiring physical contact or labels.